Table of Contents
What is the Accounting Equation?
The accounting equation considers being the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. A company’s balance sheet shows that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its obligations and shareholders’ equity.
Founded on this double-entry system, the accounting equation safeguards that the balance sheet leftovers “balanced,” and each admission made on the debit side should have corresponding access (or coverage) on the credit side.
Understanding the Accounting Equation
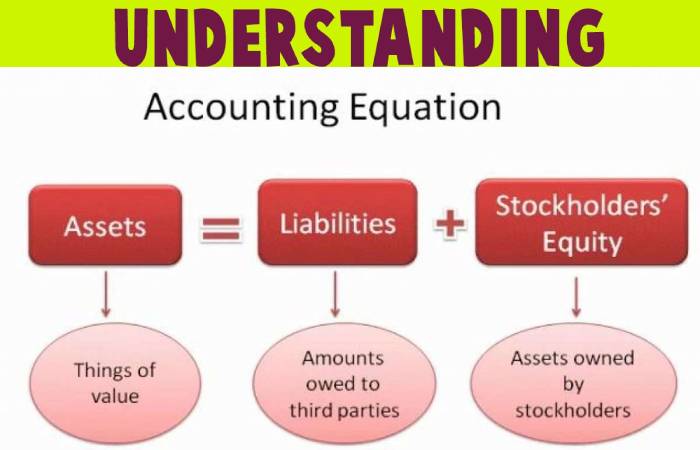
Any business’s financial position, large or small, is assessed based on the balance sheet’s two critical components: assets and liabilities. Owners’ equity, or shareholders’ equity, is the 3rd unit of the balance sheet.
The accounting equation is a picture of how these three critical components are associated with each other. The accounting equation is also called the rudimentary accounting equation or the balance sheet equation.
While assets represent the valuable resources skilful by the company, the liabilities represent its obligations. Both liabilities and shareholders’ equity signify how the assets of the company finance.
If it finances through debt, it’ll show as a liability, and if it funds from issuing equity shares to investors, it’ll offer in shareholders’ equity.
The accounting equation helps assess whether the company’s business transactions accurately reflect in its books and accounts. Below are examples of substances listed on the balance sheet:
1. Assets
- Assets comprise cash and cash equivalents or liquid investments, including Treasury bills and certificates of deposit.
- Accounts receivables are the quantity of money owed to the company by its customers to sell its product and service. Inventory is also considered an asset.
2. Liabilities
- Liabilities are what a company characteristically owes or needs to pay to keep the company running.
- Debt, counting long-term debt, is a liability, as are rent, taxes, utilities, salaries, wages, and dividends owed.
3. Shareholders’ Equity
- Shareholders’ equity is a company’s total assets disadvantage its total liabilities. And also, Shareholders’ equity signifies the amount of money that would return to shareholders if all of the assets liquidate and all of the company’s debt pay off.
- Retained earnings share shareholders’ equity and are equal to the sum of total revenues that not pay to shareholders as bonuses.
- Think of booked earnings as savings since it signifies a cumulative total of profits that have been saved and put aside or retained for future use.
Also Read: What is a Company? – Works, Types, and 10 Steps to Start-Up
Accounting Equation Formula and Calculation

The balance sheet holds the foundation of the accounting equation:
- Locate the company’s total assets on the balance sheet for the period.
- Total all liabilities, which must be a separate listing on the balance sheet.
- Locate total shareholder’s equity and enhance the number to total liabilities.
- And also, Total assets will equivalent to the sum of liabilities and total equity.
As an example, let’s say for the financial year, leading retailer XYZ Corporation stated the following on its balance sheet:
- Total assets: $170 billion
- Total liabilities: $120 billion
- And also, Total shareholders’ equity: $50 billion.
- If we compute the accounting equation’s right-hand side (equity + liabilities), we reach at ($50 billion + $120 billion) = $170 billion, which matches the value of the company’s assets.
Forms of Accounting Equation
- The accounting equation forms the basis of double-entry accounting. And also, it is a concise representation of a concept that expands into the elaborate, expanded, and multi-item display of a balance sheet.
- The balance sheet base on the double-entry accounting system. And also, a company’s total assets are equal to the total liabilities and shareholder equity.
- Essentially, the representation equates all capital (assets) uses to all sources of capital, where debt capital principals to liabilities, and equity capital principals to shareholders’ equity.
- For a company keeping detailed accounts, every single business transaction will represent at least two of its funds.
- For instance, if a business receipts a loan from a financial entity like a bank, the borrowed money will raise its assets. And also, the loan liability will increase by an equivalent amount.
- If a commercial buys raw material by paying cash, it will increase the inventory (asset) while reducing cash capital (another purchase).
- Because there are two or more accounts pretentious by every transaction carried out by a business, the accounting system refers to double-entry accounting.
- The double-entry practice safeguards that the accounting equation always remains balanced, meaning that the equation’s left side value will always match the right side value.
- All assets’ total quantity will continuously equal the sum of liabilities and shareholders’ equity in other arguments.
- The global devotion to the double-entry accounting system makes the account keeping and tallying procedures much more comfortable, standardized, and fool-proof to a reasonable extent.
- The accounting equation ensures that all admissions in the books and records vet and a verifiable relationship exists between each liability (or expense).
- And also, its corresponding source; or between each article of income (or asset) and its head.
Limits of the Accounting Equation
Although the balance sheet always equilibria out, the accounting equation doesn’t deliver investors with information about how well a company performs.
Instead, investors must understand the numbers and decide whether they have too many or too few liabilities, not sufficient assets. Or perhaps too many assets, or is funding the business adequately to ensure long term growth.
Below is a helping of Exxon Mobil Corporation’s (XOM) balance sheet in millions as of Dec. 31, 2019:
- Total possessions locate at $362,597;
- Total liabilities remained $163,659;
- And also, Total equity was $198,938.
The accounting equation, whereby assets = liabilities + shareholders’ evenhandedness calculate as shadows:
- Accounting equation = $163,659 (liabilities) + $198,938 (equity) generations $362,597, (which generations the entire assets for the retro).
Conclusion
The accounting equation considers being the foundation of the double-entry accounting system.
The accounting equation also demonstrates a company’s balance that a company’s total assets are equal to its liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
Assets represent the valued resources controlled by the company. The liabilities represent their obligations. Both liabilities and shareholders’ equity signify how the assets of the company finance.
Financing through debt shows a liability, while funding through issuing equity shares appears in shareholders’ equity.
Also Read: What is Automotive Technology? – Functions, Importance, and More
In addition, read more helpful resources at technologyies